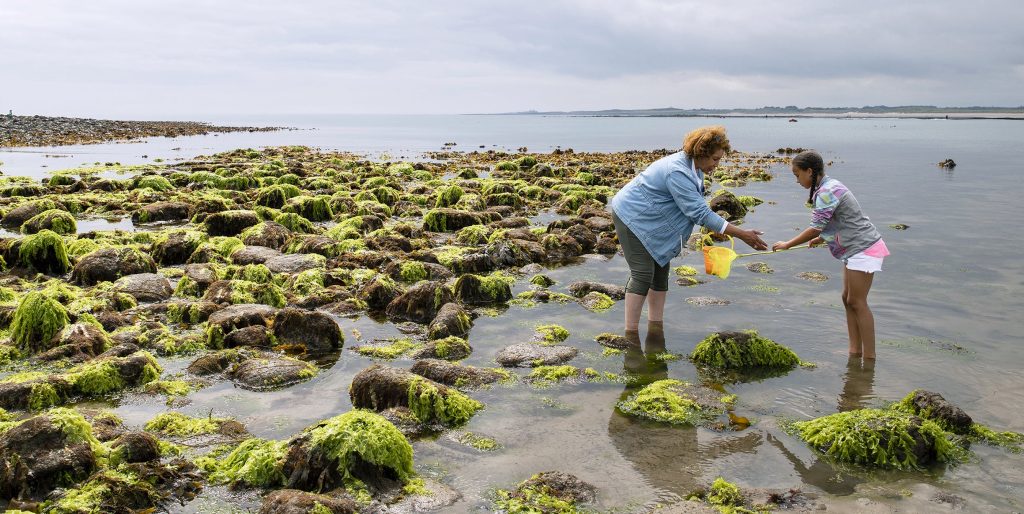

A youthful woman and her grandmother catch crabs and fish inside the shallow waters shut to Bednell Bay in northeast England. local climate change is already affecting biodiversity inside the realm: Low water availability inside the summertime, and elevated flooding and coastal erosion impacts the rich variety of habitat and species found there. photograph: SolStock
with out nature, we’re nothing. but people are destroying the environment and the residing creatures that willpower our planet dwelling at unprecedented fees — at our personal peril. From growing the specter of illness to disrupting our worldwide meals chain, biodiversity loss throughout the globe is threatening the very basis of our future and the properly-being of everyone, in each place.
The devastating outcomes of local climate change on human well being are already on current: famines triggered by as quickly as-in-a-century droughts or flooding; dying and struggling wrought by a quantity of of the strongest hurricanes and warmth waves in trendy historic previous.
however what’s much less properly-recognized is how biodiversity loss is harming our well being and threatening the important ecological cycles that maintain us alive.
“we’re out of concord with nature,” UN Secretary-frequent António Guterres instructed world leaders finally yr’s Biodiversity COP. “Humanity has show to be a weapon of mass extinction. … And finally, we’re committing suicide by proxy.”
One reporter referred to as biodiversity loss a “mounting under-the-radar disaster,” and disturbing indicators are exhibiting all through the globe, from seashores awash in sargassum seaweed to massive fish die-offs in polluted waterways. in exact fact, in response to the United Nations environment Programme, biodiversity is declining sooner than at one other time in human historic previous. proper now better than 1 million species are dealing with extinction.
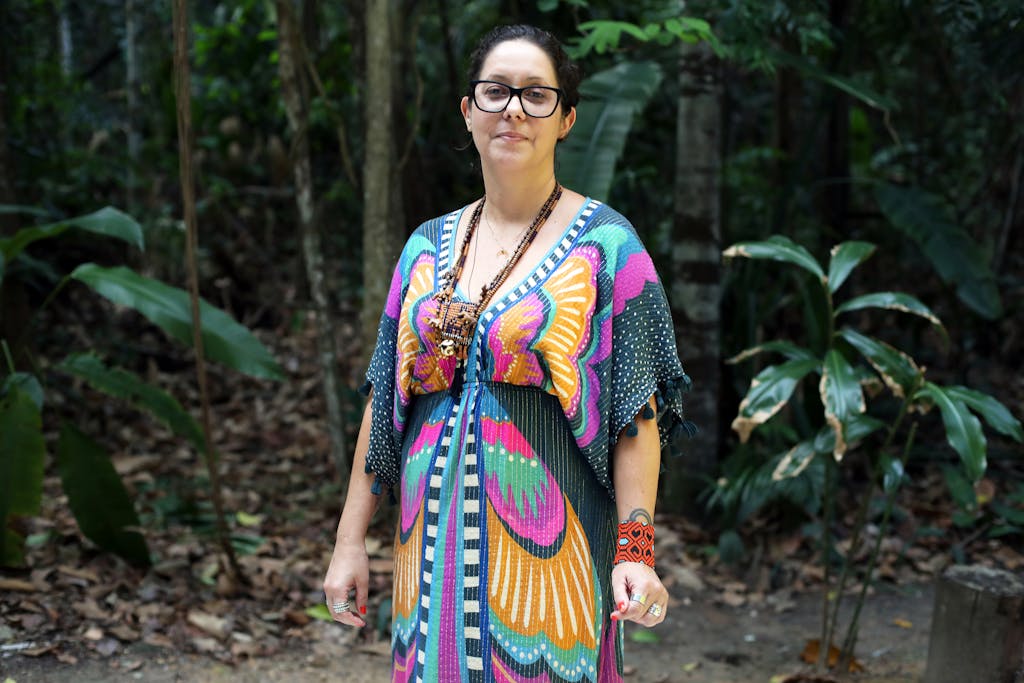

Veterinary scientist Dr. Alessandra Nava in Manaus, Brazil. photograph: Michael Dantas
inside the Amazon, a name for One well being
There are few areas on the planet the place the specter of biodiversity loss is extra evident than the Amazon, which is being destroyed by file ranges of deforestation regardless of being dwelling to one-third of the planet’s species — the best focus of biodiversity on Earth.
as a consequence of habitat destruction brings people and wildlife into nearer contact, it dramatically will enhance our menace of publicity to “zoonotic spillover,” which occurs when pathogens — micro organism or viruses that set off illness — bounce from animals to people. in exact fact, better than seventy five% of rising infectious illnesses in people are launched on by pathogens that initially circulated in animals, ensuing in tens of millions of deaths every yr. in response to some estimates, as many as 1.6 million viruses are contained inside mammals and birds throughout the globe, a quantity of of which might very properly be lethal if or as quickly as they show to be transmissible to people.
Dr. Alessandra Nava, a veterinary scientist primarily based inside the Brazilian metropolis of Manaus, has made the rainforest her laboratory. She has devoted her profession to amassing samples from small mammals for the Fiocruz Amazônia Biobank, a evaluation assortment she helps oversee as a aspect of a rising effort to hint the unfold of zoonotic pathogens, and maybe finally assist predict and even cease one other pandemic.
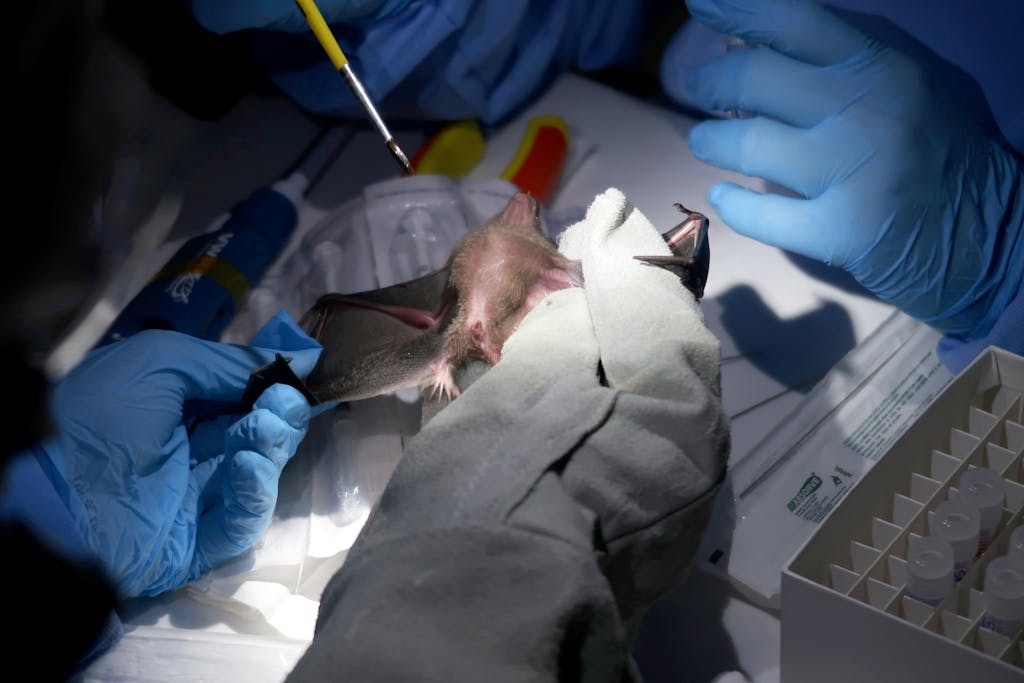
Veterinary researcher Dr. Alessandra Nava attracts a blood pattern from a bat captured shut to Manaus, Brazil. Her work is a aspect of a rising effort to hint the unfold of zoonotic illnesses inside the Amazon rainforest as deforestation brings people and wildlife into nearer contact. photograph: Courtesy of Alessandra Ferreira Dales Nava
Her work exemplifies a holistic strategy, fittingly dubbed “One well being,” that acknowledges the indivisible hyperlink between animal, human, and environmental properly-being. The UN-led initiative brings collectively the whole public well being, veterinary, and environmental sectors and promotes meals and water safety, vitamin, the administration of zoonotic illnesses, air pollution administration, and extra.
“no particular person talked about ‘One well being’ 25 years in the past,” Dr. Nava says. “as quickly as we maintain the forest intact, it serves as a buffer zone.”
defending Nature, simply as Nature Protects Us
a elevated menace of infectious outbreaks is simply definitely one of many many repercussions of biodiversity loss on human well being.
By disrupting the fragile ecological steadiness that regulates our planet’s oxygen, water, and nutrient cycles, we menace unraveling your full meals chain by harming the various completely different species — massive, small, and microscopic alike — that work collectively to pollinate, nourish, and finally maintain all of the crops and animals we devour. in response to the UN meals and Agriculture group, for event, the alarming drop inside the worldwide bee inhabitants may upend agriculture as all of us comprehend it.
Species extinction and habitat destruction additionally imply forfeiting the untapped potential of our pure world to yield new medicines for treating well being factors. in exact fact, 70% of all most cancers medicine in the present day are pure or bio-impressed merchandise. And scientists are nonetheless discovering new species every yr, collectively with a fungus that will eat plastic.
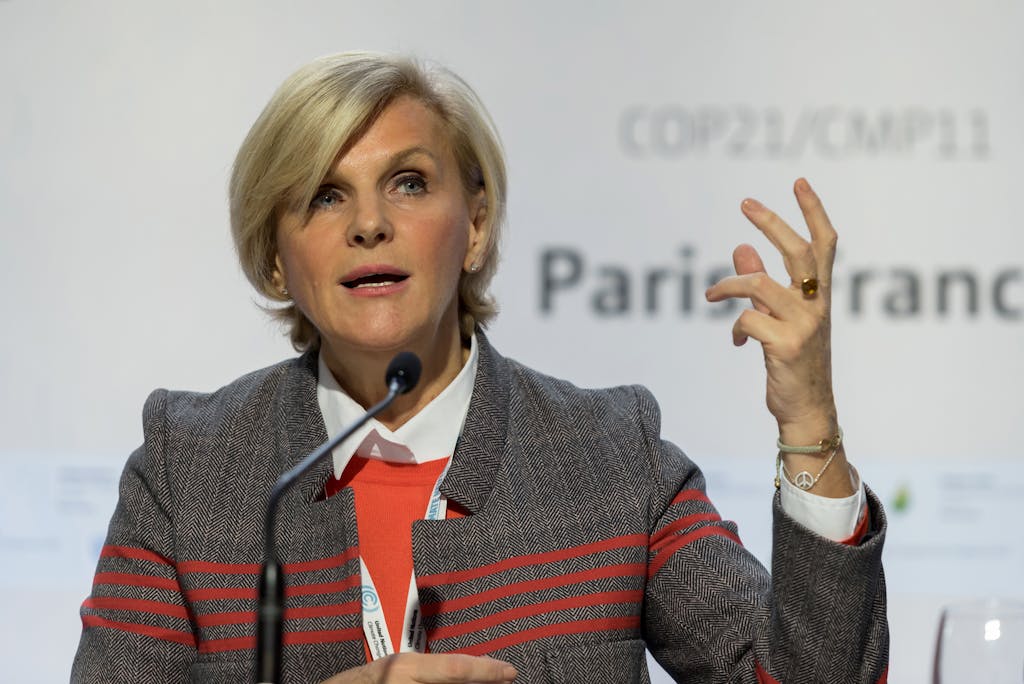

Dr. Maria Neira, WHO Director, division of Public well being, Environmental and Social Determinants of well being, delivers a speech all through the UN local climate Change convention, COP21, in December 2015. photograph: Jonathan Raa/NurPhoto
Nature additionally supplies important and usually underestimated psychological well being advantages for people. Dr. Maria Neira, Director of the division of environment, local climate Change and well being for the World well being group, witnessed this firsthand whereas working in refugee camps in Central America. There, she helped launch a mission to develop conventional medicinal herbs that helped displaced households domesticate a methodology of function, group, and sweetness in an in any other case determined state of affairs.
“You rely upon nature inside the event you’d like to survive: It provides you meals, it provides you water, it provides you bushes that will defend the customary of the air you breathe,” Dr. Neira says. “It’s frequent sense: you’d like to defend what’s defending you. If we don’t, we’re the losers, not the planet.”
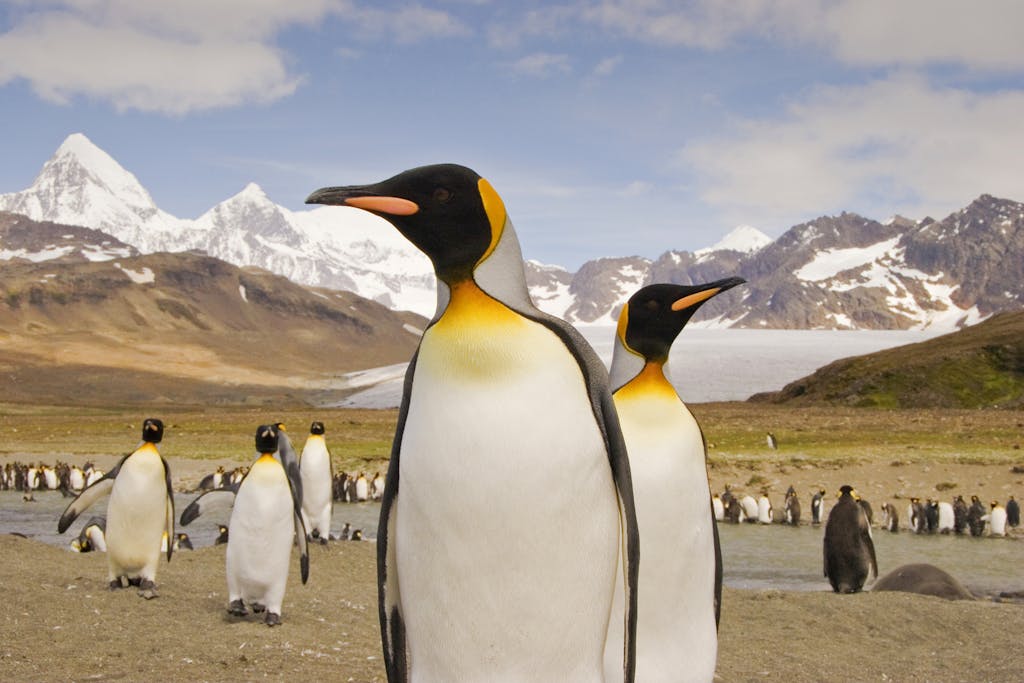

The King Penguins of South Georgia Island are an indicator species, which means that the scale and well being of their populations signifies the whole well being of their ecosystem. A healthful penguin inhabitants signifies a healthful marine ecosystem. photograph: Gen Productions
Halting the ‘Biodiversity Apocalypse’
right here’s the good information: options exist already to revive and protect the ecological properly-being of the planet. consultants and advocates have prolonged championed a quantity of essential methods to defend each biodiversity and human well being.
defending and restoring pure habitats
Conservation is important. in the present day, in response to the UN, one-third of the planet’s land is degraded, making it extra sturdy to feed a world inhabitants that not too prolonged in the past surpassed eight billion. Restoring biodiversity may additionally decelerate local climate change by storing carbon dioxide from the Earth’s ambiance. Land and ocean ecosystems presently soak up 60% of human-brought on emissions.
“Coastal and marine ecosystems like mangroves, sea grasses, and wetlands retailer methodology extra carbon than terrestrial forests, usually as a lot as 10 occasions as a lot,” says Susan Ruffo, the UN basis’s Senior Advisor for Ocean and local climate. all through hurricanes, mangroves and completely different pure habitats can additionally defend coastlines from storm surges and flooding, averting lack of life and well being impacts collectively with respiratory illnesses, publish-traumatic stress dysfunction, and infectious outbreaks that emerge after extreme climate occasions.
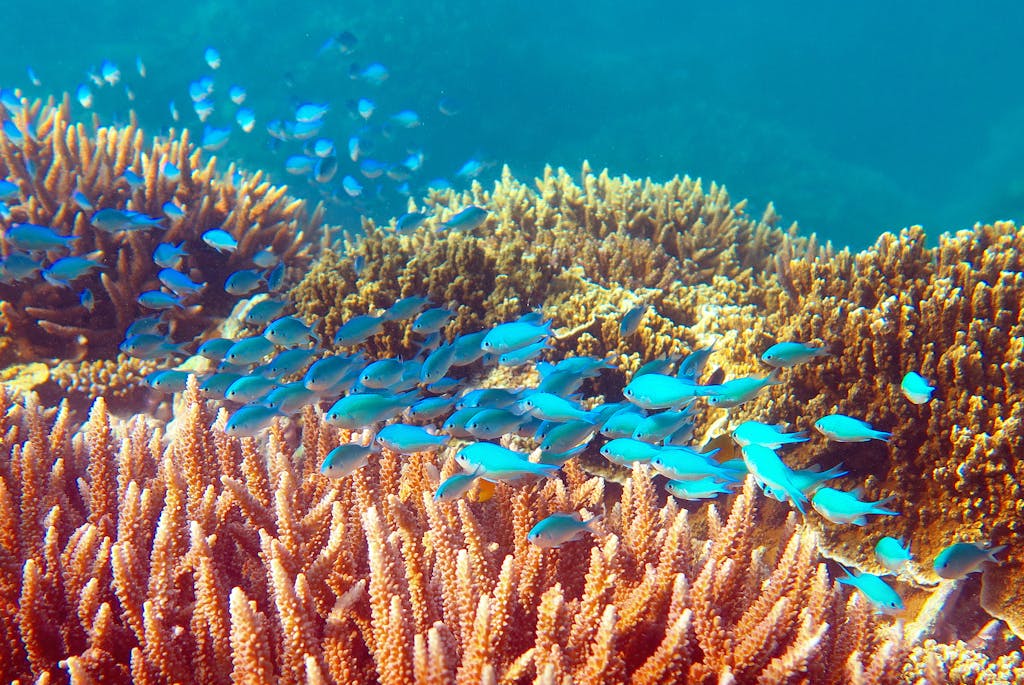

On the good Barrier Reef, a college of blue fish swims above onerous coral that is starting to bleach Coral bleaching can happen when sea floor temperatures rise or when there are modifications in water extreme quality, elevated photo voltaic publicity and extreme low tides that additionally set off corals to bleach. photograph: Matt Francey
Prioritizing island nations
Islands play an outsized function inside the planet’s biodiversity, internet hosting 20% of the Earth’s species regardless of taking on decrease than 4% of its floor space, in response to Dr. Shobha Maharaj, a local climate scientist and lead author for the most current report of the Intergovernmental Panel on local climate Change. The Caribbean, as an event, is dwelling to 10% of the world’s coral reefs and roughly 1,500 species of fish and marine mammals. These “island-endemic” species are particularly weak to habitat destruction, air pollution, and environmental modifications. in exact fact, Dr. Maharaj says eighty% of recognized species extinctions have occurred on islands. but there is a troubling absence of knowledge from these areas, Dr. Maharaj says, typically on account of insufficient funding and assets. A citizen of Trinidad and Tobago inside the Caribbean, she says extra people from island nations, notably small island growing states, should be included in worldwide willpower-making to make optimistic that their distinctive insights, as properly as to the distinctive well being threats they face, can inform worldwide coverage.
Supporting sustainable agriculture, fishing, transport, and land use
Humanity’s continued reliance on industrial practices that raze the panorama — like oil drilling, fracking, mining, and manufacturing unit farming — is destroying ecosystems whereas displacing, contaminating, and killing an limitless quantity of species. A current research found that croplands are growing fifty eight occasions as quick in the present day as they have been 20 years in the past, primarily to feed livestock amid the booming demand for meat.
one other precedence: promoting sustainable use of the ocean whereas addressing the hazards of enterprise manufacturing, consumption, and the worldwide transport commerce on life under water. Overfishing, ocean acidification, and plastic air pollution are harming marine biodiversity and, in flip, lowering worldwide fishing shares, which 1 billion people worldwide rely upon as a predominant protein supply.
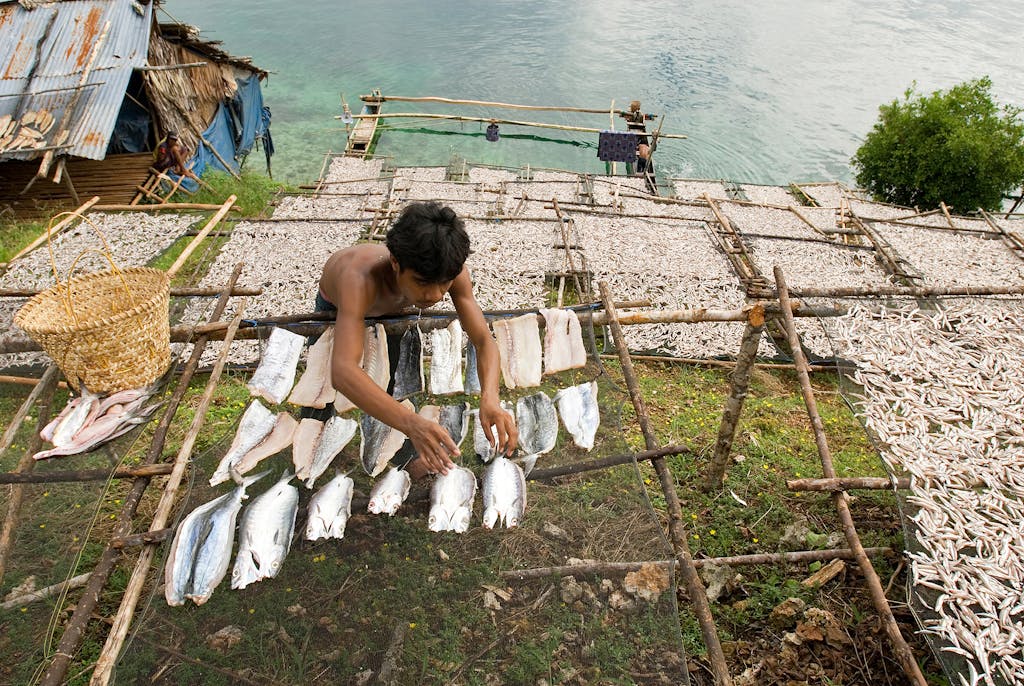

Butonese fishermen dry their catches under the photo voltaic in a quick lived fishing village they arrange on Waigeo Island, Raja Ampat Indonesia. photograph: Zafer Kizilkaya
Respecting Indigenous knowledge and rights
Indigenous people have prolonged served as a consequence of the planet’s easiest environmental stewards. in exact fact, evaluation confirms that when Indigenous communities administration the land, biodiversity thrives. but simply a few international areas acknowledge Indigenous land rights. on the identical time, given their shut relationship and reliance on nature, Indigenous communities are frequently amongst the various first to face the outcomes of biodiversity loss. That’s why safeguarding their land rights, conventional knowledge, and political illustration will in all probability be essential to defending the well being of the land, air, water, soil, and wildlife and, in flip, human well being whole.
this means incorporating Indigenous knowledge on the environment into worldwide policymaking. In Indonesia, for event, a group-primarily based coastal administration system referred to as sasi makes use of a customary calendar to get your hands on out when sure species of fish is in all probability harvested. In doing so, fishers maintain away from inadvertently depleting fish shares all through important breeding seasons and, thus, maintain native meals safety.
Now or by no means for Nature
defending worldwide biodiversity is solely too complicated to be tackled by one nation alone. current diplomatic breakthroughs akin to a consequence of the “30×30” initiative to defend 30% of the Earth’s land and water by 2030 may signal a turning level for worldwide cooperation on ecological well being.
however one factor is evident: Time is working out to take significant movement on biodiversity loss. inside the Amazon, for event, scientists warn that chopping down too many bushes may finish in your full ecosystem degrading into grasslands — an irreversible tipping level which might drastically alter how the planet circulates water and oxygen, placing human well being in hazard.
“with out nature, we have now nothing. with out nature, we’re nothing,” UN Secretary-frequent António Guterres acknowledged finally yr’s Biodiversity COP, the place he urged world leaders to rally round a plan that “beats again the biodiversity apocalypse” by tackling its root causes: unsustainable consumption and manufacturing that views ecosystems as playthings of revenue.
“It’s time,” he declared, “to forge a peace pact with nature.”
construct again BIODIVERSITY
Biodiversity connects all residing issues. due to the historic worldwide Biodiversity Framework, we have now a pathway to defending and residing in concord with nature. and everyone can play a aspect.

